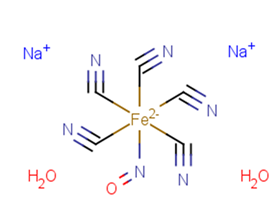
Sodium Nitroprusside Dihydrate
CAS No. 13755-38-9
Sodium Nitroprusside Dihydrate( Sodium nitroprusside dihydrate | Sodium Nitroferricyanide(III) Dihydrate )
Catalog No. M17986 CAS No. 13755-38-9
Sodium Nitroprusside Dihydrate is a potent vasodilator working through releasing NO spontaneously in blood.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 41 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSodium Nitroprusside Dihydrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSodium Nitroprusside Dihydrate is a potent vasodilator working through releasing NO spontaneously in blood.
-
DescriptionSodium Nitroprusside Dihydrate is a potent vasodilator working through releasing NO spontaneously in blood.(In Vitro):Nitroprusside disodium dehydrate sensitizes human gastric cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis.
-
In VitroNitroprusside disodium dehydrate sensitizes human gastric cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsSodium nitroprusside dihydrate | Sodium Nitroferricyanide(III) Dihydrate
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetEGFR
-
Recptorguanylate cyclase
-
Research AreaCardiovascular Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number13755-38-9
-
Formula Weight297.95
-
Molecular FormulaC5H4FeN6Na2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 46 mg/mL; 154.39 mM
-
SMILES[C-]#N.[C-]#N.[C-]#N.[C-]#N.[C-]#N.[N-]=O.O.O.[Na+].[Na+].[Fe+4]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
PF-06459988
PF-06459988 (PF06459988, PF 6459988) is a potent, selective, irreversible EGFR mutants with IC50 of 13, 7, 21 and 90 nM for EGFR L858R-T790M, Del-T790M, L858R, and EGFR Del, respectively.
-
Avitinib
Avitinib (AC-0010, AC0010) is an orally available, irreversible, and mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor with IC50 of 0.18 nM against EGFR L858R/T790M.
-
Poziotinib hydrochlo...
Poziotinib hydrochloride irreversibly inhibits EGFR (HER1 or ErbB1), including EGFR mutants, HER2, and HER4, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of tumor cells that overexpress these receptors.?It is an orally bioavailable, quinazoline-based pan epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR or HER) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity.?



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


